Are you tired of sluggish smartphones that feel like relics from the past? Android devices are racing ahead with cutting-edge features, while iPhones seem stuck in a time warp.
Yet millions of consumers still clutch their Apple devices, defying technological logic and driving tech enthusiasts crazy.
This isn’t just another tech rant. It’s a deep dive into why iPhones continue to captivate users despite falling behind in specs, innovation, and competitive edge.
We’ll unravel the psychological, marketing, and ecosystem tricks that keep Apple’s smartphone empire thriving.

iPhone’s Technological Limitations: A Critical Examination
Modern smartphone landscapes evolve rapidly, yet Apple seems to be treading water. Technological constraints have become increasingly apparent, challenging the brand’s reputation for cutting-edge innovation.
1: Sluggish Refresh Rate Performance
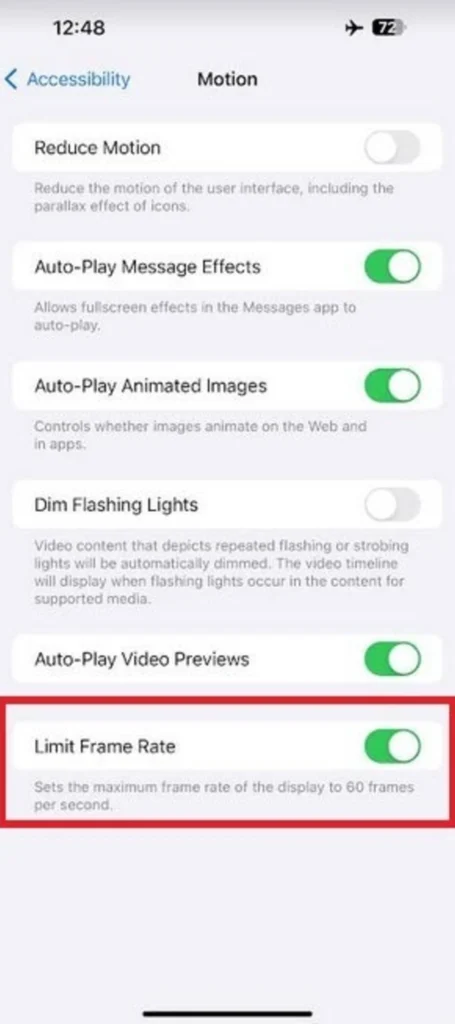
Modern smartphone users demand smooth, responsive interfaces. Apple’s base iPhone models continue to feature 60 Hz displays, a refresh rate that feels antiquated when budget Android smartphones offer 90 or 120 Hz screens.
Technological smoothness matters significantly for user experience. Consumers notice screen responsiveness during scrolling, gaming, and general navigation.
Higher refresh rates create more fluid interactions, reducing visual stuttering and enhancing overall device performance. Apple reserves advanced 120 Hz technology for premium models, creating an artificial barrier between standard and professional device capabilities.
2: Charging Speed Bottleneck

Charging technology represents another critical area where iPhones lag behind contemporary Android devices. Apple’s commitment to slow charging speeds starkly contrasts the rapid charging capabilities of competitive smartphones.
Technological constraints become evident when comparing charging wattages. While iPhones typically charge around 20W, numerous mid-range Android smartphones support 120W charging speeds.
This significant disparity means Android users can rapidly replenish battery life, whereas iPhone users endure substantially longer charging times. Such limitations impact user convenience and potentially reduce device usability during critical moments.
3: Feature Adoption Hesitation
Innovation requires the timely integration of emerging technologies. Apple’s approach to feature adoption appears methodical, often resulting in delayed implementation of industry-standard capabilities.
Consumers observe prolonged waiting periods for features like USB-C, always-on displays, and customization options. This cautious strategy contrasts with Android manufacturers’ willingness to quickly experiment and introduce cutting-edge technologies.
While Apple emphasizes polished implementations, the extended timeline can frustrate technologically aware users seeking immediate access to advanced functionalities.
4: Design Stagnation Challenge
Visual differentiation drives smartphone market dynamics. Apple’s design philosophy has become increasingly predictable, with minimal variations across recent iPhone generations.
Aesthetic consistency might represent brand recognition, but it can also signal creative exhaustion. Recent iPhone models demonstrate remarkable similarities, making it challenging to distinguish between devices released in 2019 and 2023.
This design homogeneity potentially reduces consumer excitement and perceived innovation, creating opportunities for competitors to introduce more visually distinctive smartphones.
5: Product Lineup Limitations
Smartphone diversity attracts consumers with varied preferences and budgetary constraints. Apple’s restricted product range contrasts with Android manufacturers’ extensive offerings.
Market segmentation requires a nuanced approach. While Apple provides limited models, the Android ecosystem presents multiple options across price points and feature sets.
This diversity allows consumers to select devices matching specific requirements, whereas Apple’s lineup demands compromise or significant financial investment. Restricted variety potentially alienates budget-conscious and feature-seeking consumers.
6: Persistent Design Elements

Certain design characteristics become emblematic of technological evolution. Apple’s approach to interface elements like notch and dynamic island demonstrates both innovation and limitation.
Visual elements communicate technological sophistication. The transition from traditional notch to dynamic island represents incremental progress, yet remains substantially larger than competing design solutions.
This approach suggests a conservative design philosophy, prioritizing familiarity over radical transformation. Consumers increasingly seek sleek, minimalist interfaces that maximize screen real estate.
Apple’s Innovation Strategy: A Strategic Approach
Apple’s technological journey represents a calculated approach to market evolution. Their strategy balances cautious innovation with strategic market positioning.
1: Waiting for Polish Features
Apple’s methodical feature implementation reflects a strategic approach to technological advancement. Rather than rushing unrefined technologies, they meticulously refine emerging innovations.
Technological refinement requires careful consideration and extensive testing. By observing market reactions and competitor implementations, Apple identifies potential pitfalls and opportunities.
Their approach minimizes initial technical challenges, ensuring smoother user experiences. Consumers benefit from more stable, well-integrated features that demonstrate a thorough understanding and implementation of emerging technologies.
2: Learning from Competitors’ Mistakes
Market evolution presents continuous learning opportunities for technology companies. Apple strategically observes and analyzes competitors’ technological experiments and failures.
Technological risk management involves careful study of industry developments. Companies like LG demonstrated the dangers of rapid, unfocused innovation through inconsistent product strategies.
Apple leverages these observations, creating more stable technological trajectories. Their approach allows careful selection of features with proven utility, avoiding experimental technologies that might compromise user experience or device reliability.
3: Prioritizing Reliability over Rapid Innovation

Consumer trust forms the cornerstone of technological brand success. Apple emphasizes consistent performance and dependable user experiences over flashy, experimental features.
Technological reliability requires comprehensive testing and measured implementation. By focusing on core functionalities that genuinely enhance user interactions, Apple maintains a reputation for consistent quality.
Their strategy involves deeply understanding user needs and creating solutions that address fundamental technological challenges. This approach attracts consumers seeking stable, predictable technological experiences.
4: Creating Perceived Value
Marketing represents a crucial component of technological product positioning. Apple excels at transforming technical specifications into compelling consumer narratives.
Perception management goes beyond technical specifications. Through sophisticated marketing techniques, Apple transforms hardware limitations into unique selling propositions.
Their communication strategy reframes technological choices as intentional design decisions, making consumers view potential constraints as strategic advantages. This approach allows them to maintain premium pricing and brand exclusivity.
5: Ecosystem Lock-in
Technological ecosystems create powerful consumer retention mechanisms. Apple’s interconnected product strategy encourages sustained brand engagement.
Integrated product experiences offer significant consumer advantages. By creating seamless interactions between iPhones, MacBooks, iPads, and other devices, Apple generates compelling reasons for users to remain within their technological ecosystem.
Each product enhancement increases the overall value proposition, making switching costs psychological and financial barriers for consumers.
6: Generating Upgrade Incentives

Technological progression requires continuous consumer motivation. Apple strategically designs upgrade pathways that encourage regular device replacements.
Marketing strategies transform incremental improvements into compelling reasons for device upgrades. By introducing nuanced features and subtle design modifications, Apple creates narrative momentum around technological advancement.
Their approach makes consumers feel technologically outdated, driving periodic purchase cycles. Carefully managed product launches maintain excitement and anticipation within their consumer base.
RELATED:
Competitive Landscape: Technological Evolution in Smartphones
The smartphone market thrives on continuous innovation and competitive dynamics. Manufacturers constantly push technological boundaries to capture consumer attention.
Android’s Advancement
1. Advanced Refresh Rates
Modern smartphones demand superior visual experiences. Android manufacturers have aggressively introduced high refresh rate screens, ranging from 90Hz to 240Hz, dramatically enhancing user interaction smoothness.
These technological leaps create more responsive interfaces, reducing visual lag and providing gamers and content creators exceptional screen performance.
2. Faster Charging Technologies
Charging speed represents a critical battleground for smartphone manufacturers. Android brands have revolutionized power technologies, introducing 120W and 240W charging capabilities to replenish batteries within minutes.
Consumers now expect rapid charging solutions that minimize downtime and maximize device usability.
4. Innovative Camera Technologies

Computational photography has transformed smartphone imaging capabilities. Android manufacturers integrate sophisticated AI algorithms, multiple lens configurations, and advanced sensors to create unprecedented image quality.
Brands like Vivo and Google Pixel demonstrate remarkable low-light performance and computational enhancement techniques.
4. Improved Mid-Range Phone Capabilities
Budget smartphone segments have experienced remarkable technological democratization.
Mid-range Android devices now offer features previously reserved for flagship models, including advanced processors, sophisticated camera systems, and robust build qualities. Manufacturers like Xiaomi and Realme have disrupted traditional market segmentation.
Comparative Context: LG’s Over-Innovation and Market Dynamics

LG emerged as a technological innovator, consistently introducing groundbreaking smartphone concepts that challenged market norms. Their portfolio included revolutionary devices like the modular G5, dual-screen Wing, and self-healing Flex smartphones.
Strategic missteps defined their technological journey. LG created exciting but unsustainable product lines by introducing radical features without comprehensive ecosystem support. Consumers struggled to understand the long-term value of these experimental technologies.
Ultimately, LG’s scattered approach led to market withdrawal. Their failure demonstrated a critical lesson: successful innovation requires strategic coherence, consistent user value, and sustainable development frameworks. The brand’s smartphone division collapsed, marking the end of a bold but ultimately unsuccessful technological experiment.
Current Challenges and Future Outlook for Apple
Apple confronts a pivotal moment in smartphone technology, balancing innovation with market expectations. Strategic decisions will determine the company’s ability to maintain technological leadership and consumer relevance.
Market Signals
Declining iPhone 16 Shipments
Apple’s smartphone market position faces significant challenges, with first-quarter 2024 data revealing a stark decline of nearly 10% in iPhone shipments. This translates to approximately 5 million fewer units compared to the previous year, signaling potential consumer disinterest and market saturation.
The shipment reduction reflects deeper structural issues within Apple’s current technological strategy. Consumers increasingly seek innovative features and competitive pricing, areas where Apple’s incremental updates have struggled to maintain excitement and market relevance.
Underwhelming AI Integration
Artificial intelligence represents a critical technological frontier for smartphone manufacturers, yet Apple’s current AI implementations appear tentative and less innovative compared to competitive offerings. The company’s approach seems cautious, failing to deliver truly transformative intelligent experiences.
This conservative AI strategy risks alienating tech-savvy consumers who demand sophisticated, context-aware device interactions. Competitors continue to push boundaries, creating more intelligent and responsive smartphone ecosystems.
Lack of Compelling New Features
Feature innovation drives smartphone market dynamics, but Apple’s recent product iterations demonstrate minimal technological advancement. The company struggles to generate substantial consumer excitement with incremental updates.
Smartphone users now expect meaningful technological improvements with each new release. Apple’s current approach of subtle refinements no longer satisfies increasingly sophisticated consumer expectations for groundbreaking technological experiences.
Strategic Risks
Potential Innovation Stagnation
Technological leadership requires continuous reinvention and bold strategic moves. Apple risks becoming trapped in a conservative approach that prioritizes short-term stability over transformative innovation.
Market leadership demands constant adaptation. The company’s current strategy of incremental improvements may ultimately undermine its position as a technological leader in the smartphone market.
Growing Consumer Awareness

Smartphone users have become increasingly technologically sophisticated, critically evaluating device capabilities and comparing specifications across brands. Apple’s traditional marketing strategies may struggle against more informed consumer bases.
Consumers now demand transparent technological value, pushing manufacturers to provide clear, compelling reasons for device upgrades. Apple must develop more nuanced strategies to communicate its unique value proposition.
Increasing Android Competitiveness
Competing smartphone ecosystems rapidly advance technological capabilities. Android manufacturers introduce innovative features, competitive pricing, and sophisticated user experiences that challenge Apple’s market position.
The Android ecosystem continues to offer compelling alternatives, with manufacturers like Vivo and OnePlus pushing technological boundaries. Apple must respond strategically to maintain consumer attraction and market relevance.
