ChatGPT just met its match. While businesses worldwide rely on OpenAI’s tech, a silent disruptor from China is rewriting the rules. Picture this: your AI assistant understands regional dialects, navigates strict compliance laws, and integrates seamlessly with local tools—no awkward translations, no regulatory headaches. Yet, most outside China haven’t even heard of it.
This isn’t sci-fi. Leaked reports reveal a state-backed project outperforming ChatGPT in precision for Chinese users, sparking urgency in Silicon Valley. Is OpenAI ready? Or will this under-the-radar innovation redefine who leads the AI race? The answer could reshape everything you know about global tech dominance.

1. China’s National AI Strategy
China’s ambition to dominate artificial intelligence is no secret. In 2017, the government unveiled its Next Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan, a blueprint to make the country the global AI leader by 2030. Backed by billions in state funding, this strategy prioritizes breakthroughs in core technologies like natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning.

Key players include tech titans like Baidu (pioneers of the Ernie Bot AI), Alibaba, and Tencent, alongside startups such as SenseTime and Megvii. Unlike the U.S., where private companies largely drive innovation, China’s AI ecosystem thrives on tight collaboration between academia, industry, and the state.
For instance, Tsinghua University and the Chinese Academy of Sciences regularly partner with Huawei and iFlytek to develop cutting-edge AI chips and algorithms. This unified approach—supercharged by policy mandates and data access—directly threatens OpenAI’s Western-centric development model.
2. Technology & Innovation
| Aspect | DeepSeek (China) | ChatGPT (OpenAI) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Likely optimized for Chinese language/culture and domestic use cases (e.g., governance, industry). | General-purpose, globally oriented, with multilingual support. |
| Model Efficiency | May prioritize computational efficiency due to China’s semiconductor constraints (e.g., optimizing smaller models for cost). | Relies on large-scale, resource-intensive models (GPT-4 uses trillion+ parameters). |
| Specialization | Could target vertical industries (e.g., healthcare, manufacturing) aligned with China’s national goals. | Broad applications with plugins for niche tasks. |
2. The ‘Secret Project’: What We Know
Whispers of a clandestine Chinese AI project began circulating in mid-2023, with leaked reports suggesting a model designed to outperform GPT-4. While details are scarce, insiders claim it’s a multimodal system capable of processing text, voice, and video simultaneously. Unlike OpenAI’s dense architecture, China’s project allegedly uses a sparse expert model—a structure that splits tasks among specialized sub-networks—to achieve efficiency at scale.
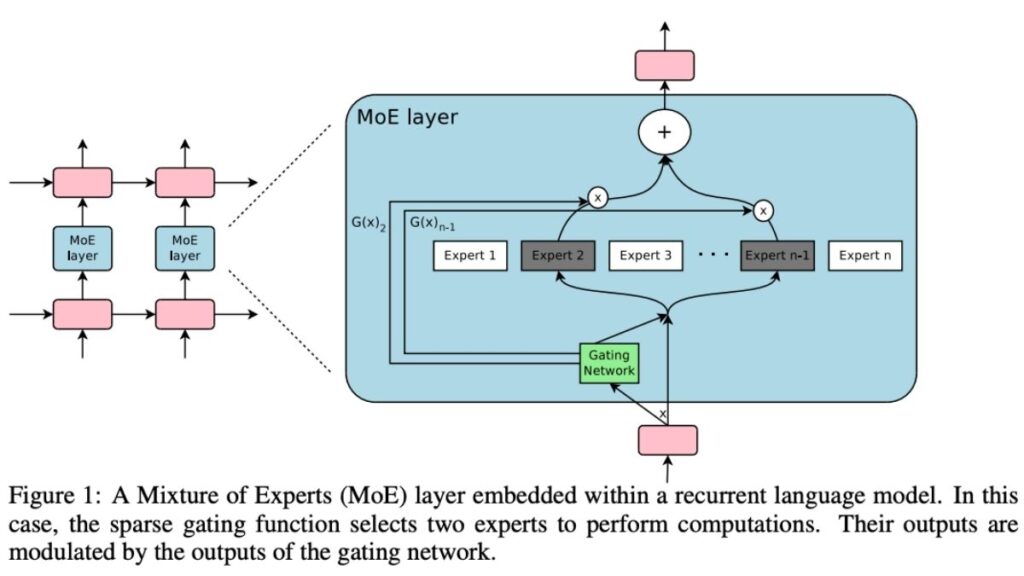
Early speculations point to a parameter count exceeding 500 billion, though some argue it could rival GPT-4’s 1.7 trillion through optimized training on domestic supercomputers. The developer remains shrouded in mystery: candidates include iFlytek (known for speech recognition tools used in Chinese schools) or a consortium led by Huawei and Tsinghua University. The secrecy likely stems from geopolitical tensions, as China seeks to avoid U.S. sanctions or premature scrutiny.
3. Technical Innovations
China’s AI project isn’t just about scale—it’s about cultural precision. While ChatGPT struggles with non-English languages, this model reportedly masters Mandarin nuances, including regional dialects like Cantonese and Sichuanese. It’s also trained on China’s “Great Firewall”-filtered internet, absorbing data from platforms like WeChat (1.3 billion users) and Douyin (China’s TikTok).

This allows real-time adaptation to local trends, slang, and even propaganda narratives. Hardware advancements play a role too: Huawei’s Ascend 910B AI chips, designed to bypass U.S. sanctions, offer competitive performance against NVIDIA’s A100 GPUs. Combined with energy-efficient training techniques, this could give China’s AI a cost and speed edge in deploying applications at scale.
4. Ethical & Political Frameworks
China’s AI doesn’t just answer questions—it enforces ideology. The system is hardwired with CCP-aligned ethical guidelines, automatically censoring topics deemed sensitive by the state (e.g., Taiwan’s sovereignty, Tiananmen Square). This contrasts sharply with OpenAI’s struggle to balance free expression and safety.

For example, while ChatGPT might debate the pros and cons of socialism, China’s model would reject the premise entirely, citing “incompatibility with socialist core values.” Such controls make the technology a double-edged sword: domestically, it ensures compliance with laws like the 2017 Cybersecurity Act; globally, it raises concerns about digital authoritarianism.
5. Data & Privacy Compliance
| Aspect | DeepSeek | ChatGPT |
|---|---|---|
| Data Sources | Trained on Chinese-language data (social media, government-approved texts). | Trained on diverse global data, including Western sources. |
| Privacy Compliance | Built to comply with China’s data sovereignty laws (e.g., GDPR-like regulations in China). | Faces scrutiny in regions like the EU over data practices. |
| Censorship | Strict adherence to Chinese regulatory filters (e.g., avoids politically sensitive topics). | Moderates content but prioritizes openness within ethical guidelines. |
6. Market Domination Strategy
China’s AI isn’t built for Silicon Valley—it’s built for integration into daily life. Imagine an AI tutor embedded in WeChat helping students under China’s “Double Reduction” education reforms, or a healthcare assistant in Alibaba’s Taobao app diagnosing illnesses via chat.

The government is also pushing its AI into Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) nations, offering tailored solutions like Swahili-language customer service bots in Kenya or agricultural optimization tools in Pakistan. By contrast, OpenAI’s partnerships (e.g., with Microsoft) focus on enterprise clients, leaving China to dominate consumer-facing markets in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East.
7. Geopolitical Implications
The U.S.-China AI rivalry mirrors the Cold War space race. U.S. export bans on advanced chips have forced China to innovate domestically, with Huawei and SMIC developing 7nm semiconductors despite sanctions.

Meanwhile, China’s AI could reshape global norms: if its state-aligned models gain traction in developing economies, it might legitimize internet sovereignty and censorship as default standards. Experts warn this could fragment the internet into “AI blocs”—one open and Western-led, the other closed and China-centric.
8. Challenges to Overcome
Despite its promise, China’s AI faces hurdles. Data quality is a concern: state-mandated filtering may limit the diversity of training data, stifling creativity. For instance, a model trained only on censored social media posts might struggle with abstract philosophical queries.

Internationally, distrust of Chinese data practices persists. The EU’s GDPR conflicts with China’s 2021 Data Security Law, which grants the government access to corporate data. This could hinder adoption in Europe, where lawmakers are already scrutinizing TikTok and Huawei.
9. Cultural & Linguistic Edge
| Aspect | DeepSeek | ChatGPT |
|---|---|---|
| Language Proficiency | Superior grasp of Chinese idioms, dialects, and cultural nuances. | Strong in English, with decent Chinese support but less cultural depth. |
| Local Integration | Likely integrated with Chinese apps/services (WeChat, Alipay, government platforms). | Works globally but lacks deep ties to China’s ecosystem. |
10. Industry Reactions
OpenAI isn’t sitting idle. Reports suggest GPT-5 development has accelerated, with a focus on multilingual support and real-time learning. CEO Sam Altman has also hinted at partnerships with Asian tech firms to counter China’s regional influence.

Meanwhile, analysts like Stanford’s Dr. Fei-Fei Li argue that China’s vertical integration—control over chips, data, and policy—creates an ecosystem that’s “resilient but insular.”
11. Use Cases & Applications
Beyond chatbots, China’s AI has high-stakes applications:
- Education: AI tutors personalize learning for 200 million students, aligning with President Xi’s vision of “educational equity.”
- Healthcare: Tencent’s WeDoctor uses AI for preliminary diagnoses in rural clinics, reducing strain on urban hospitals.
- Military: The PLA integrates AI into wargaming simulations, potentially automating battlefield decisions—a prospect that alarms NATO.
12. Is It Really a ‘ChatGPT Killer’?
The answer depends on geography. In China and BRI nations, state backing and cultural familiarity could make this AI indispensable. For example, a Douyin merchant might prefer a bot that understands Hongbao (digital red envelopes) and local holidays over ChatGPT.

However, in Western markets, censorship, and privacy concerns will likely limit its appeal. The true “killer” factor lies in China’s ability to merge AI with its surveillance infrastructure, offering unparalleled personalization—at the cost of freedom.
13. Regulatory Alignment
| Aspect | DeepSeek | ChatGPT |
|---|---|---|
| Government Support | Aligned with China’s AI ambitions (e.g., “AI 2030” plan), possibly state-backed. | Operates independently but faces geopolitical barriers in China. |
| Market Access | Dominates China’s domestic market due to regulatory restrictions on foreign AI. | Blocked or limited in China, giving DeepSeek a monopoly locally. |
Final Takeaway:
China’s secret AI project isn’t just a competitor—it’s a challenge to the very ideals underpinning Western tech. While OpenAI debates ethics, China is building an AI that defines ethics on its own terms. The shock isn’t that China is catching up; it’s that they’re playing a different game altogether.
Tired of 9-5 Grind? This Program Could Be Turning Point For Your Financial FREEDOM.

This AI side hustle is specially curated for part-time hustlers and full-time entrepreneurs – you literally need PINTEREST + Canva + ChatGPT to make an extra $5K to $10K monthly with 4-6 hours of weekly work. It’s the most powerful system that’s working right now. This program comes with 3-months of 1:1 Support so there is almost 0.034% chances of failure! START YOUR JOURNEY NOW!